WHAT’S NEXT FOR THE PHILIPPINES
So, what now for the Philippines? The 19 per cent tariff rate is still lower than what other neighbouring ASEAN economies got. Vietnam got 20 per cent and Indonesia 19 per cent. Both rates are significantly lower than the April rates of 40 per cent and 32 per cent, respectively. The two countries, which are not formal military allies of Washington, fared better in their negotiations with the US compared to the Philippines, a formal US treaty ally.
Nevertheless, the US remains the biggest destination of Philippine exports (about 17 per cent of total exports), and the semiconductor industry is likely to be hit significantly. It would have been better if Marcos Jr had been able to secure a tariff exemption on Philippine semiconductors. Still, other vulnerable sectors include garments, food, and agricultural products – as suggested by the experience during the trade war during the first Trump administration.
Looking for a silver lining, the Philippine government hopes that some trade from higher-tariffed countries may be diverted to the Philippines because of the country’s relatively lower tariff rate. But this is unlikely given the country’s lack of competitiveness.
This is due to ongoing deficits in the country’s logistics and transportation infrastructure, overreliance on low value-added parts of global value chains, and worrying gaps in human capital. During the previous Trump administration’s trade war, these constraints did not help the Philippines become an alternative trade partner and investment destination.
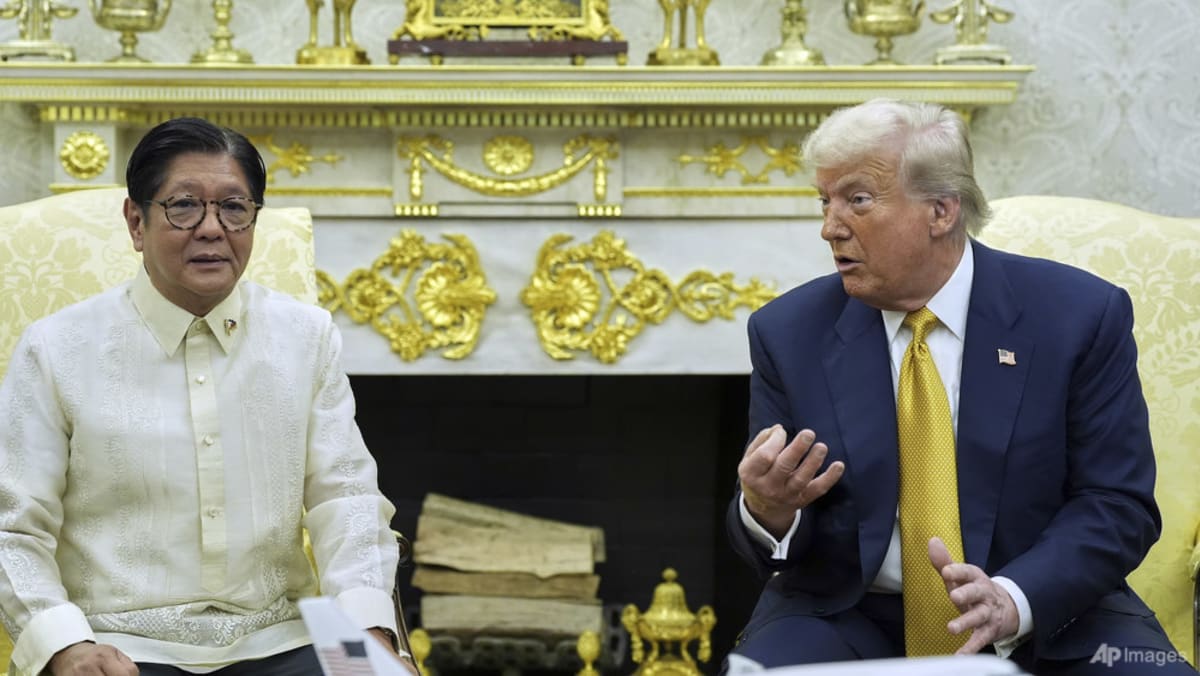
On Monday (Jul 28), Marcos Jr will deliver his fourth State of the Nation Address, and he is likely to brag about the profuse praise he got from Trump as well as the new tariff rate. With the Philippines ending up with an even higher tariff than in April, that hardly points to Marcos being a “very good, very tough” negotiator.
The outcome of the US trip should serve as a powerful signal to the Marcos Jr administration. As it started to diversify its security relations beyond the US alliance by deepening cooperation with middle powers such as Japan and Australia, it must do the same to promote its economic interests. Under Trump 2.0, it might be wise for the Philippines not to put all its economic eggs in the US basket.
JC Punongbayan is an assistant professor at the University of the Philippines School of Economics and Aries A Arugay is Visiting Senior Fellow and Coordinator of the Philippine Studies Programme at ISEAS – Yusof Ishak Institute. This commentary first appeared on ISEAS – Yusof Ishak Institute’s blog, Fulcrum.